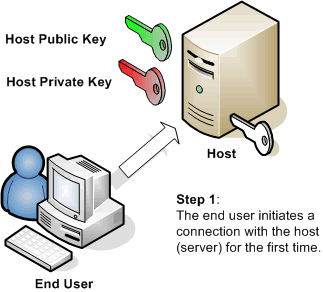
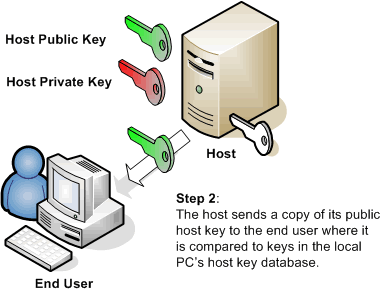
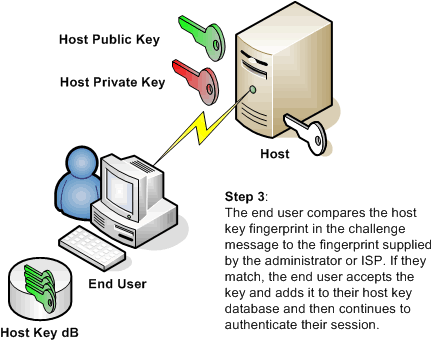
Users and administrators turn to Secure Shell for many reasons. Some need to replace Telnet or FTP. Others are looking to move away from simple passwords to public-key, Kerberos, or keyboard-interactive authentication. Still others are looking for a low cost alternative to VPNs. Whatever the reason for using Secure Shell, every user and administrator of Secure Shell needs to understand host keys. Understanding what host keys are, how they work, and the security they provide can reduce confusion and possible frustration about administering and using this authentication tool for both administrators and end users.
Failure to understand host keys can cause many problems. Some users may be frightened or confused by messages when a new or changed host key is encountered. This can result in additional and unnecessary support costs. Even worse, improper handling of host keys can lead to a compromised system.